叶片形态是植物适应环境的重要特征,其复杂性(如小叶数量及边缘锯齿)受生长素(auxin)和细胞分裂素(cytokinin)信号通路的协同调控。生长素通过其合成基因(如YUC家族)及转运蛋白(如PIN1)在叶原基形成局部浓度峰值,驱动小叶和锯齿的起始;而细胞分裂素通过调节形态发生窗口期影响叶片复杂度。草莓(Fragaria vesca)的典型复叶由三片小叶组成,但调控其形态的具体分子机制尚未完全阐明。前人研究发现,草莓中FveYUC4通过调控生长素合成影响小叶锯齿深度,而FveCUC2a通过调控叶缘分离和锯齿形成参与形态建成。FveMYB117a作为MYB转录因子,此前被报道通过调控细胞分裂素代谢基因(FveIPT2和FveCKX1)抑制侧芽萌发,但其在叶片发育中的功能及与生长素、细胞分裂素通路的关联仍不清楚。
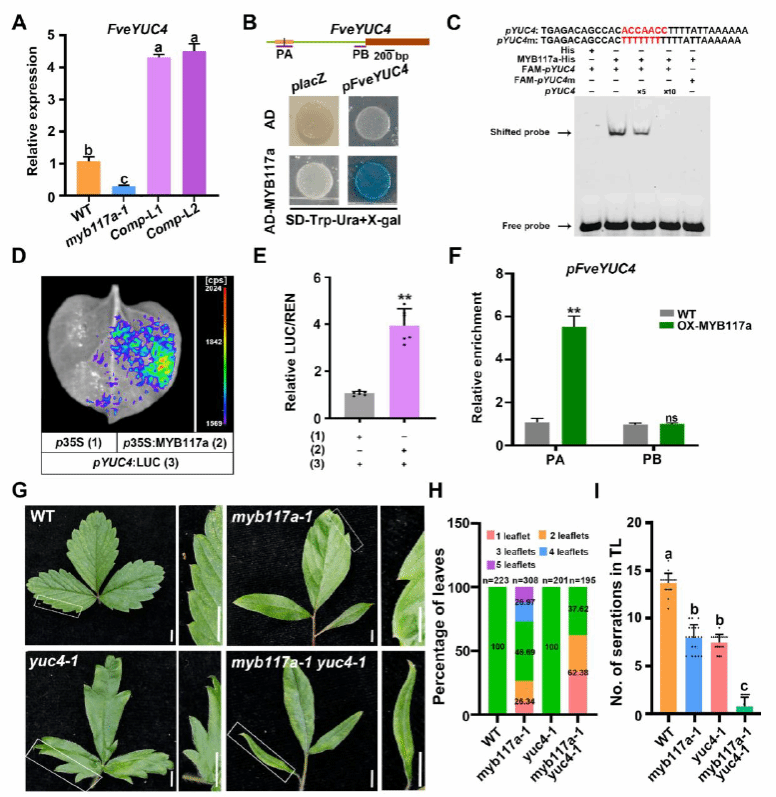
华中农业大学康春颖团队通过研究揭示了FveMYB117a通过直接调控生长素合成基因FveYUC4和转录因子基因FveCUC2a的表达,协调生长素与细胞分裂素稳态,从而控制草莓叶片复杂性的分子机制。FveMYB117a突变体(myb117a)表现为叶片小叶数量异常且锯齿减少,同时茎尖组织中生长素(IAA)水平显著降低,活性细胞分裂素(iP、cZ、tZ)水平升高。转录组分析显示,myb117a中FveYUC4和FveCUC2a表达分别显著下调和上调,且KNOXI类基因(如FveSTMa、FveBP)表达异常升高。通过酵母单杂交(Y1H)、电泳迁移率变动分析(EMSA)及染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP-qPCR)实验证实,FveMYB117a直接结合FveYUC4启动子的PA片段并激活其表达,同时结合FveCUC2a启动子的PA/PB片段并抑制其转录。双荧光素酶报告系统(Dual-LUC)进一步验证了FveMYB117a对FveCUC2a启动子的抑制作用。遗传互作实验表明,myb117a yuc4双突变体中额外小叶表型被抑制,而myb117a cuc2a双突变体则完全丧失小叶分离和锯齿形成能力,表明FveYUC4和FveCUC2a是FveMYB117a调控叶片形态的关键下游靶点。外源施加生长素运输抑制剂NPA可使myb117a叶片简化为单叶,而施加细胞分裂素(6-BA)则增加额外小叶比例,证实激素平衡对表型的调控作用。
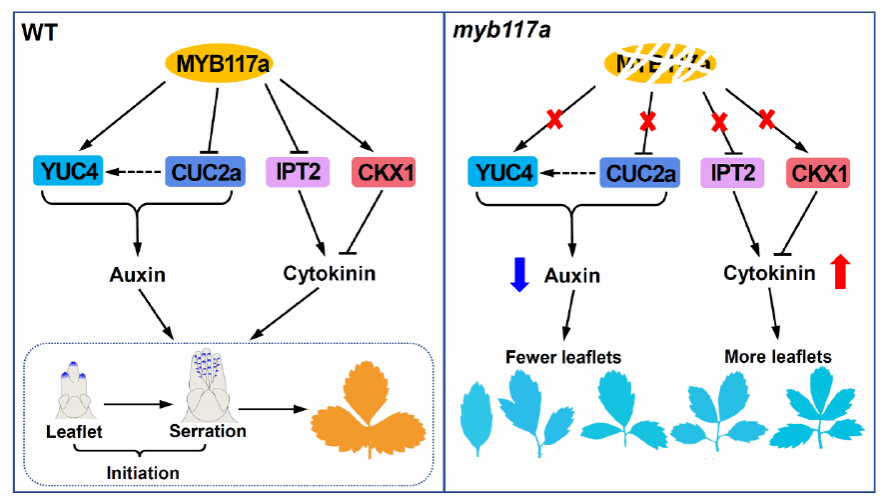
本研究阐明了FveMYB117a通过直接调控FveYUC4(生长素合成)和FveCUC2a(叶缘发育)的表达,协调生长素-细胞分裂素动态平衡,进而精确控制草莓叶片复杂性的分子网络。这一机制不仅揭示了MYB转录因子在激素互作中的核心作用,还为改良作物叶片形态及抗逆性提供了新的分子靶点。
文献:
Plant Physiol., 16 Apr 2025
The transcription factor FveMYB117a controls leaf morphology by coordinating auxin and cytokinin signals in woodland strawberry.
Author
Han Y, Lu R, Yan D, Liu Z, Luo X, Kang C*.
*: National Key Laboratory for Germplasm Innovation & Utilization of Horticultural Crops, Huazhong Agricultural University, China.
Abstract
Leaf morphology affects physiological activities and contributes to environment adaptation. The phytohormones auxin and cytokinin both regulate leaf shape, but how they act together to specify leaf complexity is not fully understood. In woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca), the wild type develops trifoliate leaves, whereas myb117a mutants produce one to five leaflets with fewer serrations. Transcriptome analysis revealed that the auxin biosynthesis gene YUCCA4 (FveYUC4), the cytokinin biosynthesis gene ISOPENTENYL TRANSFERASE2 (FveIPT2), the cytokinin degradation gene CYTOKININ OXIDASE/DEHYDROGENASE1 (FveCKX1), and the transcription factor gene CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON2 (FveCUC2a) are altered in the myb117a mutant. Accordingly, the myb117a leaves contain lower auxin levels and higher cytokinin levels compared to wild type. Moreover, treatment with the auxin transport inhibitor NPA produced simple leaves with smooth margins, whereas exogenous cytokinin application resulted in a higher percentage of four to five leaflets in myb117a. Several lines of evidence showed that FveMYB117a can directly bind to the promoters of FveYUC4 and FveCUC2a and influence their expression. Both myb117a yuc4 and myb117a cuc2a double mutants had fewer leaflets with greatly reduced or no serrations compared to myb117a, suggesting that these genes function in the same pathway. Overall, our results indicate that FveMYB117a is a transcription factor that coordinates auxin and cytokinin homeostasis in young leaves, thereby contributing to robust leaf morphogenesis in strawberry.
原文转自:公众号:莱肯生物(华农康春颖团队鉴定草莓叶形改良关键调控因子)

